Mode of Action of Calcific Barbotage
Calcific barbotage works by mechanically breaking down and removing calcium deposits within the tendon. These deposits cause pain, inflammation, and restricted movement. During the procedure, a fine needle is inserted into the calcified area under ultrasound guidance. The needle is moved repeatedly within the deposit—a technique called “barbotage”—to disrupt and fragment the calcium. The loosened fragments are then aspirated (drawn out) through the needle.
Remaining calcium particles are gradually absorbed by the body over time, reducing inflammation and pain, and allowing the tendon to heal and regain function.
Calcific Barbotage
Calcific Barbotage is an advanced, minimally invasive procedure used to manage pain and restore function in patients suffering from calcific tendonitis. This treatment targets calcium deposits that commonly form within tendons, particularly in the shoulder’s rotator cuff. The procedure is performed under ultrasound guidance to ensure precision and patient comfort, making it an effective option when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief.
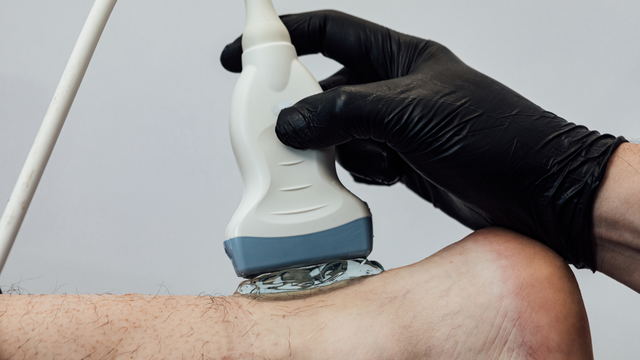
Procedure of Calcific Barbotage
Ultrasound Guidance: The affected tendon is scanned to precisely locate calcium deposits.
Local Anaesthesia: The area is numbed to ensure patient comfort throughout the procedure.
Needle Insertion: A fine needle is carefully guided into the deposit using real-time ultrasound imaging.
Barbotage: The needle is moved repeatedly within the deposit to break it down into smaller fragments.
Aspiration: The calcium fragments are aspirated out of the tendon.
Post-Procedure Care: The area is cleaned and dressed. Patients are usually advised to rest and avoid heavy use of the joint for a short period.
This outpatient procedure typically takes around 45 minutes, allowing patients to go home the same day.
Ultrasound-Guided Calcific Barbotage
Ultrasound guidance significantly enhances the safety and accuracy of calcific barbotage by providing real-time imaging. This ensures precise targeting of the calcium deposits while avoiding nerves, blood vessels, and other surrounding tissues. Ultrasound also enables the clinician to monitor the effectiveness of the deposit removal during the procedure.
Conditions Treated with Calcific Barbotage
Calcific Tendonitis
Calcific tendonitis is characterised by painful calcium deposits within a tendon, often causing inflammation, stiffness, and limited range of motion. Symptoms include sharp pain during movement or at night, tenderness around the joint, and in severe cases, chronic discomfort affecting daily activities.
Benefits of Calcific Barbotage
Minimally Invasive: Performed using a fine needle, reducing the need for surgery and promoting faster recovery.
Precision: Ultrasound guidance ensures targeted treatment for improved outcomes.
Pain Relief: Removal of calcium deposits alleviates irritation and discomfort.
Improved Function: By clearing deposits, the tendon can heal, improving joint mobility over time.
Calcific barbotage is typically recommended when conservative treatments such as physiotherapy, medications, or steroid injections have not been effective.